| January 18, 2018 | SNORT - IDS / IPS can be installed from Zeroshell 3.7.1 allowing to identify and block attacks from outside to the LAN. |
| 29 December 2017 | The new Zeroshell 3.8.2 for X86 / X86_64 and ARM contains the latest versions of OpenVPN and nDPI, improved hardware recognition and other Bug Fixes. |
| December 14th 2017 | An image of Zeroshell 3.8.1A for Orange Pi PC Plus has been released. This model is more convenient than the Orange Pi PC because in addition to having in addition a working Wi-Fi module both as Client and Access Point, it also has a Flash memory Integrated MMC which allows Zeroshell to be installed when it is not necessary to use a MicroSD. |
| November 16th 2017 | An image of Zeroshell 3.8.1A for Orange Pi R1 has been released. This small and economical Quad Core device has two 10/100 Ethernet interfaces and a Wi-Fi module that works both as a Client and Access Point. |
| November 2, 2017 | Zeroshell 3.8.1 has a more stable kernel that solves the problem of sporadic system crashes. Patches have been applied to the wireless system against the latest vulnerabilities of the WPA2 protocol implementation. Other fixes have been applied and in particular the VPN system is more reliable. Zeroshell 3.8.1 is available for both X86 architecture and ARM architecture. |
| 7 July 2017 | Zeroshell 3.8.0 has a new Kernel and several Bugs and Security Fixes. The update to this release is recommended. |
| April 29th 2017 | Zeroshell 3.7.1A is the first release for ARM Architecture. At the moment only the following platforms are supported: Raspberry Pi 2/3, Orange Pi Zero, Orange Pi PC and Orange Pi Plus / Plus2. |
| January 20th 2017 | An exploit has been identified that allows the execution of unauthorized remote code. Several installations were already compromised. It has become urgent to upgrade to Zeroshell 3.7.1 which neutralises this security flaw. Any version prior to 3.7.1 is vulnerable. |
| January 5th 2017 | Zeroshell 3.7.0 has a new kernel with which some stability problems have been solved and performance improved. Many services including Captive Portal, VPN and Radius have been recompiled with the new OpenSSL 1.0.2 libraries. This was necessary because the old OpenSSL 0.9.8 are no longer supported and have different vulnerabilities. The compatibility of the Captive Portal and RADIUS server with new client devices has also been improved. |
| 4 December 2016 | Ipt-netflow is available for Zeroshell 3.6.0 which allows you to export network traffic statistics to a NetFlow / IPFIX collector. ipt-netflow operates in Kernel mode, thus guaranteeing high performance. |
| October 20th 2016 | NTOPng is available for Zeroshell 3.3.2+. It allows you to view and analyze network connections by ordering them by busy bandwidth, exchanged traffic, application (L7 protocols) and more. For more information visit http://www.ntop.org |
| September 21st 2016 | A development environment is available for Zeroshell that allows you to install applications by compiling the sources. To be installed, it requires at least Zeroshell 3.3.2 and is available through the Package Manager. It can also be used to compile the Kernel or individual driver modules that best support your hardware. |
| 4th of July 2016 | Zeroshell 3.6.0 solves some problems related to Captive Portal, VPNs and Net Balancer. The web interface of the Firewall and of the Traffic Shaping has been changed to support nDPI which will soon replace the L7 Filters as a Deep Packet Inspection system. Improved hardware support thanks to Kernel 4.4.13. In particular, Intel NICs on PCIe buses take advantage of this release. |
| 3 March 2016 | Zeroshell 3.5.0 includes the new GLIBC 2.23 libraries that solve the vulnerability described by CVE-2015-7547 regarding previous versions that would allow, through specific responses of a DNS controlled by hackers, to take control of the system. Therefore, the upgrade is strongly recommended. This release includes Kernel 4.1.15 which guarantees better performance and lower latency with a significantly reduced Load Average. |
| January 10th 2016 | Kernel 4.1.15 is available. This Kernel guarantees better recognition and management of new hardware. It has been configured with some parameters concerning the frequency and the scheduling strategy that have made it more performing and with lower latency in the networking operations. Using this kernel you notice a significant decrease in system load. |
| 2 December 2015 | PHP and MySQL are available for installation as an Add-On from the Repository. |
| 2 October 2015 | Zeroshell 3.4.0 has a new kernel with improved recognition and support for next-generation hardware. Improved performance and fixed numerous bugs. Guaranteed Wireless connectivity for iPads and iPhones upgraded to the latest iOS 9 .
The update can be done online via the Package Manager without having to reinstall. |
| March 1, 2015 | With the new Kernel available in the repository it is now possible to create Virtual Machines hosted by Hypervisor XEN. This is a 64-bit Kernel and therefore it is not possible to create 32-bit virtual machines. |
| 1 February 2015 | All Zeroshell releases up to 3.3.1 include a version of the GLIBC libraries that is vulnerable to possible buffer overflows. This vulnerability, called GHOST, could allow remote execution of unauthorized code. For these reasons, it is recommended to upgrade to Zeroshell 3.3.2 which includes the latest version of the GLIBC as well as several other fixes. |
| January 25th 2015 | Zeroshell 3.3.0 includes the Kernel 3.14.29, numerous Bug Fixes and some improvements of the Web interface. The CNTop utility has been integrated, which can now sort and display the hosts that consume more band as well as generate more connections. A problem with the Net Balancer Failover system has been corrected. Also this release has the 64 Bit Kernel which improves its performance and allows to use all the available RAM. Accessing the repository is possible to upgrade automatically from the 3.0.0 release. |
| 20 January 2015 | A 64-bit Kernel is available that provides better performance for Kernel Mode processes such as Firewall, Routing, Bridging, Traffic Shaping, Layer 7 Filters and Network Address Translation (NAT). |
| January 5th 2015 | A new version of the CNTop utility for Zeroshell is available.
This release, allows to know in addition to the hosts that are generating the most connections, even the IP that are exchanging more data. Moreover, the reverse resolution from IP to hostname is available that allows to identify the hosts more easily and to quickly understand the type of traffic that occurs on its LAN.
IP filters, protocol and port number are applicable. |
| 29 September 2014 | The new Zeroshell 3.2.0 release is now available.
It is imperative to upgrade to this new release because all the above are affected by a serious vulnerability caused by a Bash bug (CVE-2014-7186 vulnerability ShellShock). By exploiting this vulnerability, an unauthenticated user can execute arbitrary code from the web interface.
Many other bugs have been corrected. |
| September 14th 2014 | An incorrect configuration of the Connection Tracking prevented the Layer 7 Filters from working correctly. All releases starting from 2.0.RC1 to 3.1.0 present such a malfunction.To solve this problem install the BugFix Package 23102 on Zeroshell 3.1.0. This package also eliminates the limit of 100 Free Authorized Clients of the Captive Portal. |
| July 15, 2014 | The new Zeroshell 3.1.0 release is now available. With this release the stability of the system has improved and many bugs have been fixed. Among the new features, there are some important ones such as:
- The Installation Manager that allows an installation easier and faster than before, starting from CD or USB Flash or using an existing installation.
- Weighted Bonding that allows you to balance traffic on links with different speeds.
- The Monitoring and Alerting system via e-Mail / SMS that monitors the occurrence of certain events such as the absence of a network. The list of events can be extended and the managers of customized events.
- The CNTop utility that displays the IP addresses with the most TCP / UDP connections open at the same time. This can be used effectively to determine a host from which a DDoS attack is coming from or to its own network.
Among other things, the Captive Portal has been improved and now allows a greater number of users connected at the same time.
If the 3.0.0 release is already installed and access to the active repository, it is possible to upgrade to 3.1.0 automatically, without losing the configuration and with a few simple clicks. The package to be installed from the repository is 53100 which will take care of the migration with a minimum interruption of service due to the reboot. If you want to use the Installation Manager instead, remember that all data on the destination disk will be destroyed. It is therefore necessary to first make a backup of the profile and then the subsequent restoration on the new installation. |
| 10 May 2014 | The new Monitoring and e-Mail / SMS Alerts Suite monitors some critical events that may occur. Each Event is assigned a level of severity on which the choice of recipients of Alert messages via e-mail and / or SMS is based. Severity levels are: Info, Warning, Critical and Emergency.
It is available as a New Feature for Zeroshell 3.0.0 and is essential for rapid intervention in resolving critical events in a production environment. |
| January 25, 2014 | The new Zeroshell on disk installation procedure is available, which allows greater speed and reliability than direct writing of the disk image with the dd or equivalent command.Moreover, the Install Manager automatically adapts the partition of the profiles to the size of the disk avoiding having to perform additional steps to expand the partition.
In a production environment, you should always choose the version of Zeroshell installed on disk because it is faster and more reliable than the Live CD version.
The details are at the URL: http://www.zeroshell.net/installation-manager/ . |
| January 13, 2014 | A new bonding mode available as New Feature for Zeroshell 3.0.0 has been implemented.
With the weighted bonding it is possible to distribute the traffic in proportion to the capacity of the interfaces forming part of the bond. Before the introduction of this feature, the distribution of traffic took place with a simple Round-Robin that treated the interfaces in a uniform manner regardless of the actual available bandwidth. The direct consequence of this was that one could benefit from bonding only if the aggregate lines had similar capacity. It could be seen that adding a 2Mbit / s ADSL line with a 7Mbit / s line was in a band close to only 4Mbit / s. Far from the desired result.
Now with Weighted Bonding, just assign to the first ADSL line a weight of 2 and the second one a weight of 7, to see an aggregate band very close to the sum of the two lines. It should be noted that in the example we have intentionally omitted, for simplicity, to specify that the bonding of WAN lines makes sense only through VPN bonding and therefore the weight must be assigned to the VPNs in layer 2. |
| January 2, 2014 | Zeroshell 3.0.0 includes substantial innovations including the automatic update system that automatically applies security and bug fixes and allows updating to new releases.Security has been improved and numerous bugs fixed. Charts no longer require the activation key. There are numerous Kernel optimized for different processors and a Kernel compiled with PAE (Physical Address Extension) that allows you to use more than 4GB of RAM. |
| 7 August 2013 | With the 2.0.RC3 version of Zeroshell some security issues are corrected. In particular, DNS now caches and accepts recursive queries only for local networks if not configured otherwise. Lately DNS open completions have been targeted for DDoS attacks with consequent bandwidth consumption. For this reason the migration to 2.0.RC3 is strongly recommended.
No-IP has been added as a provider for dynamic DNS and the recognition of 3G USB modems has been improved. It is now possible to disable virus scanning of web pages resulting in improved transparent proxy performance on modest hardware.
Several Fixes have been applied to the Profile Backup / Restore procedure. |
| November 21st 2012 | Zeroshell 2.0.RC2 improves support for balancing and fault tolerance of multiple Internet connections. In particular, this release allows to maintain in Standby the PPPoE (xDSL) and UMTS / HSDPA connections, activating the PPP protocol only in the absence of connectivity from other accesses. These connections are again placed in Standby when the connectivity returns from the default accesses. Improved Failover with controls in Layer 2 as well as with ICMP. VPN Bonding for bandwidth aggregation and LAN-to-LAN failover updated. Fixed various bugs throughout the system. In particular, in the Captive Portal a problem was solved that caused blocking under high load conditions. |
| 25 July 2012 | Zeroshell 2.0.RC1 has a new kernel (3.4.6) that allows better recognition of the latest hardware. The Wi-Fi section has been updated, which uses the ath9k kernel module to support the 802.11n standard (thanks to Arth for the contribution to update the wifi-manager). The atheling patch is included which allows you to use QoS and Net Balancer at the same time. In addition to OpenVPN, IPSec / L2TP, you can use PPTP as a VPN for users whose authentication can be delegated to an external RADIUS. Numerous bugs have been fixed throughout the system with particular regard to the Captive Portal. |
| September 10th | Version 1.0.beta16 corrects some problems of the Captive Portal that delay the opening of the authentication page on the browsers that perform checks through CRL or OCSP.The mechanism to restore the LDAP DB in case of corruption after a crash has been improved.
Support has been added for Shibboleth as a Service Provider that redirects the authentication of the Captive Portal to Identity Provider belonging to standalone or federated AAI. |
| July 15, 2011 | The new 1.0.beta15 release contains the RADIUS Accounting module that allows you to account for time, traffic and connection costs both for access points on the Access Point with WPA / WPA2 Enterprise and Captive Portal. You can set limits in traffic and time and manage prepaid rates. The Captive Portal has been enriched with new features such as protection against DoS attacks and the ability to disable the Popup window for access to the network on mobile devices. |
| January 16th 2011 | Zeroshell version 1.0.beta14 is available. Contains many bug fixes and web interface improvements. Many packages have been recompiled with a new compiler (gcc 4.5.2).Thanks to the elimination of some causes of segmentation fault, stability has improved. |
| 2 July 2010 | The new 1.0.beta13 release from Zeroshell is now available, including: a preview of the accounting system for the accounting of time, traffic and connection cost per user;Bandwidthd that tracks the most bandwidth consuming hosts; a series of Bug Fixes. |
| May 9th 2010 | The Samba package for Zeroshell is available to manage Windows network resources. See the post http://www.zeroshell.org/forum/viewtopic.php?t=2209 |
| May 9th 2010 | The NTFS-3G package for Zeroshell is available that allows you to mount NTFS filesystems in Read / Write. See the post http://www.zeroshell.org/forum/viewtopic.php?t=2210 |
| October 18, 2009 |
The Snort 2.8.5 package is available that allows a Zeroshell router / bridge to act as an IDS (Intrusion Detection System) and detect possible attacks / worms on its LAN. More details are available at the URL http://www.zeroshell.net/patch-details/#DA12 . |
| June 14, 2009 | The Dansguardian patch has been updated to be compatible with Zeroshell's 1.0.beta12 release.
Further details are available at the URL http://www.zeroshell.net/patch-details/#BA12 . |
| May 26th, 2009 | The 1.0.beta12 release is available. This release increases the stability and security of the system. |
| 6 April 2009 | Statistical graphs with MRTG related to network traffic (Ethernet, Wi-Fi, VLAN, PPPoE, 3G and VPN), system load, traffic shaping and gateway load balancing are available by installing the update http: //www.zeroshell. net / patch-details / # C110 |
| 9 February 2009 | The update is available http://www.zeroshell.net/patch-details/#C105 which enables Dynamic DNS to manage the tracking of dynamic IPs for OpenDNS. Further details are available at the URL http://www.zeroshell.net/opendns |
| January 11, 2009 | Security Bug - All releases up to 1.0.beta11 (included) are affected by a serious security problem that allows the execution of unauthenticated remote code.
Update the system to 1.0.beta11 and apply the patch http://www.zeroshell.net/patch-details/#C100 . |
| December 16th 2008 | Support for Multilink PPP |
| November 7, 2008 | The Asterisk VoIP PBX is available as an external package. More details are available at the URL http://www.zeroshell.net/patch-details/#C000 |
| October 12, 2008 | The 1.0.beta11 release of Zeroshell is available. The main innovation is the Net Balancer which allows to configure the Load Balancing and the Failover of Internet connections (ADSL, UMTS / HSDPA, ...). Support for VPN aggregation has been improved, which increases bandwidth and stability of Layer 2 links between remote sites. With this release we have support for 3G modems that allows Zeroshell to perform the task of UMTS / HSDPA routers. A problem of stability of the web proxy with antivirus has been solved and the overall stability of the system has been improved. |
| June 29, 2008 | Zeroshell version 1.0.beta10 is available. It contains a more updated kernel capable of handling recent hardware and, starting from this release, the boot can also take place from HD / CDROM SATA and USB. For IDE disks, it is no longer necessary for them to be configured as Primary Master. Bugs have been fixed and support for Host-to-LAN VPNs with OpenVPN and startup scripts has been improved. |
| April 28th 2008 | The pre-configured DansGuardian package is available, which cooperates with the transparent proxy service to filter out unwanted web traffic. The default configuration denies access to web pages containing adult-only material. More details are available at the URL http://www.zeroshell.net/patch-details#AA00 . |
| April 20, 2008 | A patch has been released to resolve proxy stability issues. More details are available at the URL http://www.zeroshell.net/patch-details#A500 . |
| March 30th 2008 | Released an image of Zeroshell 1.0.beta9 able to boot from a USB disk. The minimum size of the USB device is 1 GByte. It is compatible with both USB 1.1 and USB 2.0 and in particular on the latter has shown a speed of bootstrap much greater than the ISO version. |
| March 15th 2008 | Zeroshell 1.0.beta9 is available. With this release is available a transparent Web Proxy (HAVP) with ClamAV antivirus that scans web pages by blocking Virus and Worm. It is also possible to manage Blacklist and Whitelist to prevent the display of some URLs.
The Captive Portal now contains a flag that allows you to disable SSL in cases where it is not required. This allows to eliminate the warning messages regarding the digital certificates that can not be verified during user authentication.
The order in which the QoS classifier rules are evaluated has changed and Apache and OpenSSL have been updated because they were vulnerable as evidenced by Nessus. |
| January 20, 2008 | Zeroshell 1.0.beta8 is available. The main novelty is the support for WiFi that allows, to a Zeroshell box, to perform the function of Access Point with support for Multi-SSID and different types of security including WPA-PSK, WPA-EAP with Radius and WEP. In particular, multiple SSIDs can be configured both in bridges with each other and with 802.1q VLANs. Simultaneous management of multiple WiFi cards is supported on which it is possible to define SSID in load balancing. Several bugs have been fixed and in particular the Captive Portal and VPNs have been significantly improved from a security point of view. In addition, from this release the network interfaces can be configured to dynamically acquire IP addresses using a DHCP. |
| 06 December 2007 | The Kerberos tutorial http://www.zeroshell.net/kerberos/ is now available at the URL http://www.kerberos.org/software/tutorial.html as an official tutorial from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Kerberos Consortium. Zeroshell authentication is based on Kerberos 5. |
| November 28, 2007 | The ALIX.2C2 mini computer with 256MB of RAM, AMD Geode LX CPU 500MHz processor and MiniPCI expansion slot was tested with Zeroshell's WRAP CompactFlash. It is impressive the increase in performance that is achieved compared to WRAP with this new embedded platform for network appliances. |
| November 25th 2007 | A patch is available to be applied to the 1.0.beta7 release of Zeroshell that enables EAP-TTLS authentication instead of PAP for the Captive Portal users authenticated via RADIUS. EAP-TTLS, using TLS encrypted tunnels, helps to increase the confidentiality of user credentials when using RADIUS instead of Kerberos 5 which is already intrinsically safe. For more details click here . |
| November 4, 2007 | In the download section there is a package that adds Wi-Fi support to Zeroshell. Both the Client Station mode with which a Zeroshell box can be associated to a Wireless network, and the AP mode with which the actual Access Point functionality is obtained is supported. At the moment WiFi network cards (miniPCI, PCI) with Atheros Chipset are supported and can be used with the modules distributed by http://madwifi.org . For further details read the post http://www.zeroshell.net/forum/viewtopic.php?t=482 . |
| 6 October 2007 | A VMWare Virtual Machine with a pre-installed Zeroshell is available in the download section. The purpose of this version is to facilitate Zeroshell testing without investing in specific hardware, but it can also be used in the production environment. The Zeroshell Virtual Appliance has been tested with VMWare Player, VMWare Workstation and VMWare Server. |
| September 16th 2007 | The 1.0.beta7 release is available. In addition to a number of Bug Fixes, this release introduces the ability to create Host-to-LAN VPNs using OpenVPN. This type of VPN, supported by most operating systems (Linux, Solaris, OpenBSD, FreeBSD, NetBSD, Mac OS X and Microsoft Windows), supports the L2TP / IPSec VPNs that have often proved not easy to configure on the client side. With OpenVPN, ZeroShell can authenticate VPN connections with X.509 Digital Certificates, Kerberos 5 (thus also Active Directory) and RADIUS.
A configuration file for OpenVPN clients is available in the download section. |
| 11 September 2007 | ZeroShell has become a dynamic DynDNS Dynamic DNS client. Visit this page for more details. |
| August 22nd 2007 | The 1.0.beta6 release of ZeroShell is available at URL http://www.zeroshell.net/download/ . The main variants have been introduced in the Captive Portal which, in addition to Kerberos 5 authentication, now also accepts RADIUS authentication and X.509 digital certificates. This allows the use of Smart Cards for authentication with Captive Portal.
This release includes the Watcher Daemon, which is a process that verifies the correct operation of the services (LDAP, DNS, Kerberos, RADIUS, DHCP, ssh) and in case of a crash it restarts the process. FreeRadius has been updated with a version compatible with the Windows Vista 802.1x / PEAP supplicant. |
| 02 July 2007 | There is a bug in version 1.0.beta5 of ZeroShell due to which the VoIP connections made with SIP protocol may not work properly. In this case, add the command modprobe -r ip_nat_sip in the startup script from the [Setup] -> [Startup] section. |
| June 27th 2007 | The 1.0.beta5 release of ZeroShell is available at URL http://www.zeroshell.net/download/ . Contains many Bug Fixes and new features. The main novelty is the presence of the Connection Tracking Logger, which allows, if activated in the Firewall, to keep track of connections by sending logs, for each connection, the Protocol, the IP source address, the Source Port, the IP address of Destination and Destination Port. |
| April 4, 2007 | Due to a BUG, the Username and Password of users accessing via Captive Portal remain in the History of the browser. The captive portal should therefore not be used in public places where multiple people access the same browser profile. This behavior will be corrected in the 1.0.beta5 release. |
| February 18th 2007 | The 1.0.beta4 release of Zeroshell has been released. The l7-filter filters were introduced to classify the traffic by inspecting the contents of the packages at the application level.This is useful for applying QoS for protocols that can not be classified by filters on IP addresses and TCP / UDP ports such as the H323 and SIP VoIP protocols. |
| January 28, 2007 | The 1.0.beta3 release of Zeroshell has been released. The main novelty of this release is the management of QoS (Quality of Service) that allows to model traffic on a congested network thanks to the assignment of the Priority, the Guaranteed Band and the Maximum Band to the traffic classes. It has also been introduced, within the Firewall and the QoS classifier, the possibility to control traffic such as P2P File Sharing through the IPP2P module of iptables and connection tracking. |
| November 7th 2006 | After several requests I added support for the WRAP (Wireless Router Application Platform) board. These small, cost-effective computers for network appliances require a custom CompactFlash image. |
| November 2, 2006 | At URL http://www.zeroshell.net/forum/ there are forums dedicated to ZeroShell, networks in general, Linux and the network and embedded devices oriented to network services. |
| October 25, 2006 | The 1.0.beta2 version for Compact Flash is available. |
| September 24th 2006 | ZeroShell 1.0.beta2 is available for download in the ISO image format. |
| June 29th 2006 | The version for Compact Flash is available. |
| June 25, 2006 | ZeroShell 1.0.beta1 is available for download in the ISO image format. The Compact Flash version and C ++ sources will be available soon. |
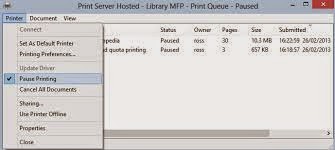 Note: sometimes the problem is much more simple and crude and just check that the print spooler of the printer in question has not been inadvertently put in "sleep".
Note: sometimes the problem is much more simple and crude and just check that the print spooler of the printer in question has not been inadvertently put in "sleep".